Introduction to the Cluster Setup¶
SeaTable can be operated both as a single-node installation and in cluster mode. The following section explains when each setup is appropriate and what advantages a cluster setup offers.
Don't be confused by the term dtable
Originally (a long time ago), SeaTable was going to be called dtable (short for database table). Although this term was later replaced with SeaTable, many internal components and log entries still use the old name dtable. Whenever you see dtable, it simply refers to a component of SeaTable.
Naming conventions¶
In the following instructions for deploying a SeaTable Cluster, I will use the node names and roles listed below as a naming convention. Please adapt these to fit your specific environment.
| Node | Main service / Name | Private IP address |
|---|---|---|
| node1 | dtable-web | 10.0.0.2 |
| node2 | dtable-db | 10.0.0.3 |
| node3 | dtable-server | 10.0.0.4 |
| node4 | dtable-server-2 | 10.0.0.5 |
| node5 | dtable-events | 10.0.0.6 |
When is a single-node installation suitable?¶
In a single-node installation, all SeaTable components run on a single server. This setup is usually sufficient for small teams and organizations with up to several hundred users and offers good performance.
However, as the number of users and the complexity of the bases increase, bottlenecks may arise. In particular, the dtable-server - responsible for rendering the bases, see the architecture of SeaTable for more details - will eventually reach its performance limits. Depending on usage intensity and base size, this can occur with as few as 100 users, or only after surpassing 1.000 users.
Typical signs of overload:
- Noticeably longer loading times when opening a base.
- The appearance of so-called kill events in the
monitor.log.
What is a Kill Event?
SeaTable checks every 30 seconds whether its individual components are reachable. If a component does not respond within 20 seconds, the corresponding service is automatically stopped and restarted. You will see such events in logs/monitor.log, for example:
[2025-07-01 11:12:56] [WARNING] Ping error, kill dtable-server
The component name (e.g., dtable-server, dtable-web, dtable-db) indicates which service was affected.
Short-term improvements can often be achieved by allocating additional resources (CPU, RAM). However, in our experience, once you reach about 8 CPUs and 32 GB RAM, further performance gains are negligible. If the dtable-server is overloaded by too many requests, even more resources cannot resolve the bottleneck, and kill events will occur.
What limits the dtable-server?
The dtable-server is implemented in such a way that loading and saving the JSON files is a blocking process that cannot be parallelized further. This creates a bottleneck that limits scalability on a single server. See the architecture of SeaTable for more details.
When is a Cluster Setup Recommended?¶
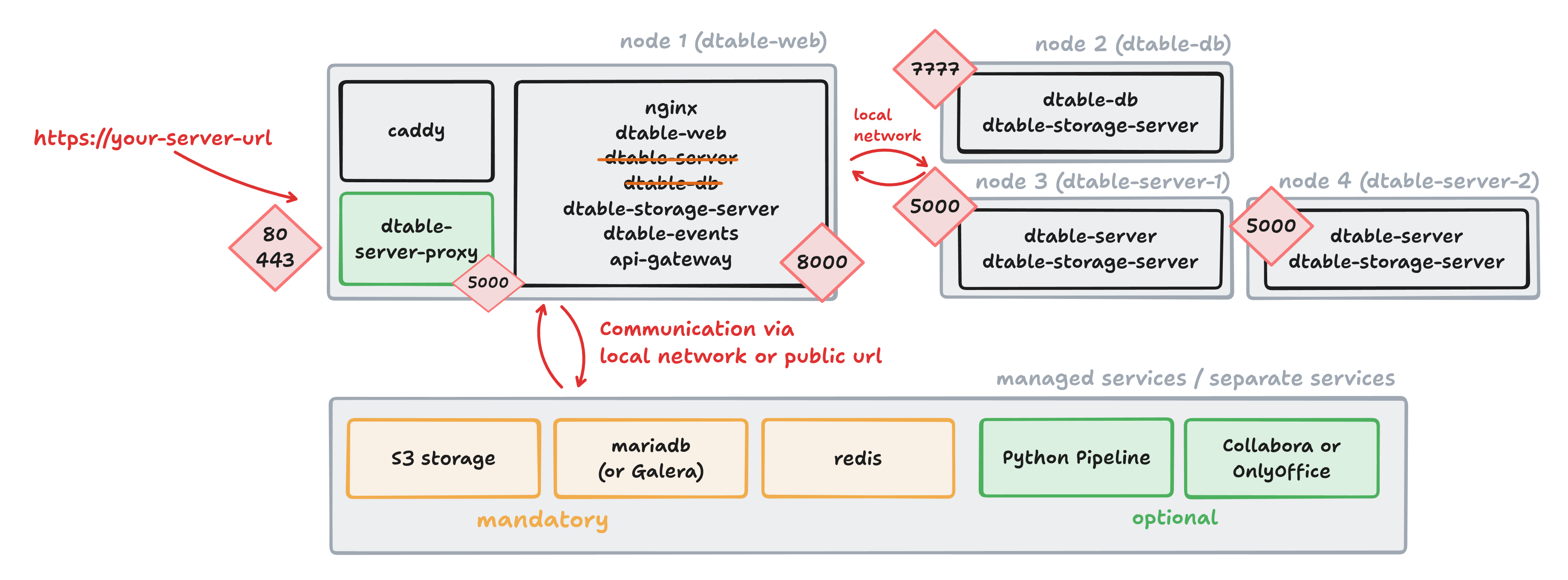
Once the single-node setup reaches its performance limits, it is advisable to switch to a cluster setup. A cluster consists of multiple nodes, each running only selected components of the SeaTable server.
Key features of a cluster setup¶
- All nodes use the same Docker image, but individual components are selectively enabled or disabled.
- The setup usually starts as a single-node installation. Gradually, individual components are moved to separate nodes.
- In the maximum expansion stage, each service runs on its own node; multiple
dtable-serversand multipledtable-webcan run in parallel. Please note that the latter requires sticky sessions.
Advantages of a cluster setup¶
- Significantly more resources available: Overall performance can be increased almost indefinitely by adding more nodes.
- Targeted allocation of CPU and RAM: Resources can be assigned to individual components as needed.
- Higher performance: Parallel operation of multiple dtable-servers allows many more users to be served simultaneously.
- Improved fault tolerance: If one node fails, other nodes can take over its tasks for highly available components like
dtable-web. For components likedtable-server, only a portion of users may be affected if multiple instances are running.
Don't underestimate the challenges to manage a cluster
While a cluster setup offers greater performance and availability, it also requires a solid understanding of distributed systems and experience in debugging. Operation is significantly more complex than with a single-node system. The following chapters will help you understand the requirements and setup of a SeaTable cluster.
Continue reading about the requirements and setup of a cluster in the next article.